Product Description
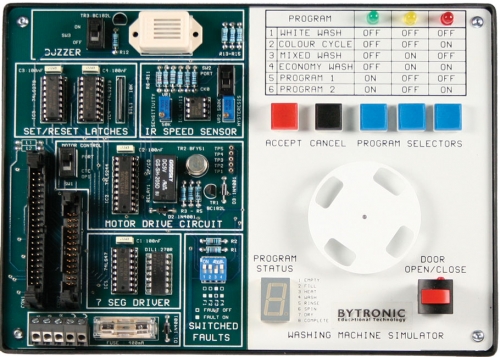
The Washing Machine Simulator (WMS) is an application for electronic control engineering. The unit incorporates a series of input and output devices, which together simulate the actions of a typical domestic washing machine. The WMS has two main areas. The first area comprises the electronic circuits and connector sockets, the second area is the indicators, a motorised disc (which represents the washing machine drum) and the user controls. The circuit board incorporates test points, a fuse and four switches for fault insertion.
Three blue push buttons are used to select a ‘wash program’ from the software program and inputs from these buttons turn on green, yellow and red LED’s. The binary pattern displayed may be compared to a ‘program selector table’ to indicate the current choice of program. A grey push button is used to cancel the current choice and a red push button to ‘accept’ input for the controller. A mechanically latched push button with a built in LED provides an input, which simulates the open/closed status of the washing machine door. An infra-red reflective sensor mounted beneath the disc supplies feedback on the speed of the motor. A seven-segment display is used to highlight the ‘wash program status’. The status options are: Empty, Fill, Heat, Wash, Rinse, Spin, Dry and Complete.
Motor speed can be controlled using PWM and a buzzer activated to indicate the end of the ‘wash program’ (can be enabled or disabled using on-board switch). The buzzer can also be used to indicate that the ‘door’ has been opened or that a fault has occurred. Variations for programming the WMS are possible using two switches that change the input/output characteristics of the motor drive and speed sensor feedback. The WMS can be connected to a PC, using a suitable interface, or to a microcontroller.
Experiments:
- Control of digital outputs
- Control of the seven segment display
- Reading the program selector switches
- On/Off control of the DC motor
- Controlling the DC motor/speed open loop
- Reading the motor speed feedback
- Colour wash program cycle
- Closed loop control of the DC motor